Executive Summary
Japan’s Hokkaido University Information Initiative Center provides High Performance Computing (HPC) and cloud computing services to researchers at the institution and across Japan. The university’s HPC resources are connected with other supercomputers around the country as part of its High Performance Computing Infrastructure (HPCI) initiative. To continue to support insight and innovation in computational research, the Information Initiative Center increased research supercomputing capacity 23X1 with installation in December 2018 of Grand Chariot (3.08 petaFLOPS) based on Intel® Xeon® Gold 6148 processors and Polaire (0.87 petaFLOPS) built on Intel® Xeon Phi™ 7250 processors—both interconnected by Intel® Omni-Path Architecture fabric.
Challenge
Hokkaido University promotes world-class computational research to solve the problems confronting humankind. The University’s Information Initiative Center takes a major role to support the activity by providing large-scale computing and networking services to researchers. The typical research run on Hokkaido University’s supercomputers includes ocean analysis, electromagnetic field analysis, weather simulation, computational chemistry, and others.
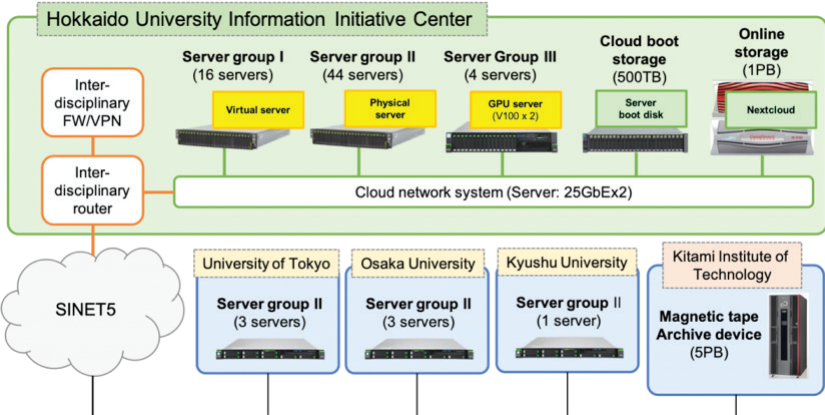
Since 2011, the university has supported scholarly studies in cloud services to promote research for the practical use of intercloud systems. Combining the results of this research and its need to expand supercomputing capacity, in 2018 it developed an interdisciplinary large-scale computer system called the High Performance Intercloud. The Intercloud includes a supercomputer system and a cloud system.
Solution
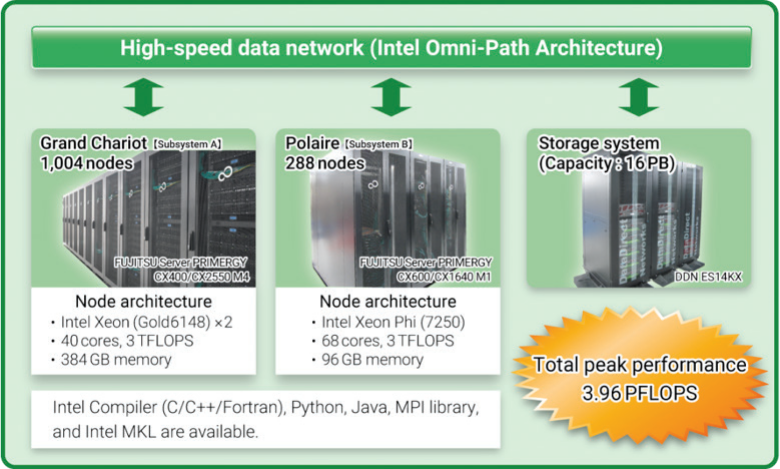
Hokkaido University’s interdisciplinary supercomputer comprises two clusters totaling nearly four petaFLOPS of theoretical performance.1 To support supercomputing applications in various scientific domains, Hokkaido University deployed a 3.08 petaFLOPS cluster called Grand Chariot. The supercomputer uses 1,004 nodes of Fujitsu PRIMERGY* CX2550 with Intel® Xeon® Gold 6148 processors (40 cores/node). Grand Chariot ranked 95 in the November 2018 Top5002. Furthermore, considering the trend of HPC technology, the Information Initiative Center installed a 288-node cluster called Polaire. It uses Fujitsu PRIMERGY* servers with Intel® Xeon Phi™ 7250 processors. Polaire will be used to develop an advanced simulation code which efficiently utilizes many-core processors.
Both clusters are interconnected by 100 Gbps Intel® Omni-Path Architecture (Intel® OPA) fabric and supported by a Data Direct Networks 16 petabyte Lustre* storage system. Each node in Grand Chariot includes two Intel OPA host fabric adapters to support increased injection bandwidth and to ensure continued job execution if a switch fails.